Healthy sleep cycles
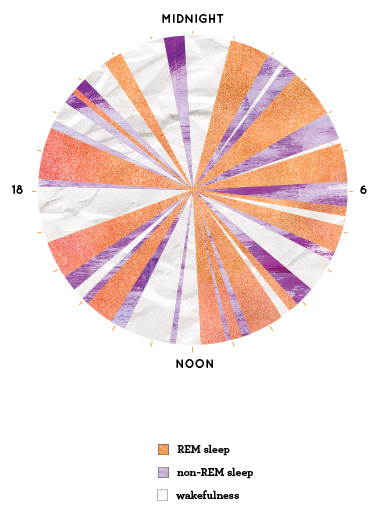
To fully understand how narcolepsy affects the brain, first you must learn a bit about how a normal brain works…
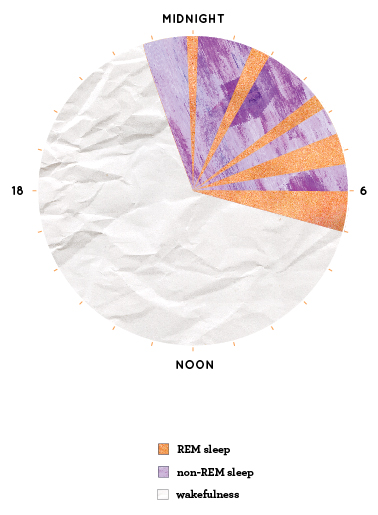
A healthy person will get around 6-8 hours of sleep on average, and in this time they will go through several “stages” of sleep. There are two main categories for these stages: REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep and non-REM sleep. A normal sleep cycle will go through stages 1-4 before moving into REM, and then alternating between
Non-REM sleep makes up 75% of a normal sleep cycle and consists of stages 1-4, each typically lasting for 5-15 minutes. Stages 1 and 2 are the lighter stages of sleep, occurring just as a person begins to fall into sleep. Stages 3 and 4 are our stages of deep sleep, also known for being the “delta wave” or “restorative” sleep stages.
During these stages brainwaves slow considerably and the body has time to truly rest and repair itself: relaxing and increasing blood flow to muscles, slowing breathing and heart rate and releasing hormones essential for growth and repair.
REM sleep makes up the remaining 25% of a normal sleep cycle and typically occurs about 90 minutes after the onset of sleep. It is during this stage that most dreaming occurs; our brains are very active (sometimes more so than when we are awake), our eyes dart around rapidly, and our bodies are paralysed to prevent us from physically acting out our dreams.